PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
7240-38-2 (Sodium)
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
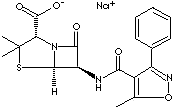
[2S (2a, 5a,
6b)]-3.3-dimethyl-6-[[(5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl) carbonyl]
amino]-7-oxo-4-thia-1- azabicyclo [3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, monosodium
salt.
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Some organisms are penicillin-resistant because they produce an enzyme
called penicillinase, that destroys the antibiotic. Oxacillin, derived from
6-aminopenicillanic acid, is a semisynthetic penicillinase-resistant penicillin
against staphylococci primarily. New penicillins such as methicillin, (di)cloxacillin,
flucloxacillin
and
oxacillin are not destroyed by the penicillinase, but have no effect on bacteria
that are resistant by other means like by altered cell wall structure. Macrolide
antibiotics that inhibits protein synthesis by bacteria have become important in
treating penicillin-resistant infections in patients allergic to penicillin. The
sodium salt of oxacillin is administered orally, intramuscularly, or
intravenously. Chemical designation is [2S (2a, 5a,
6b)]-3.3-dimethyl-6-[[(5-methyl-3-phenyl-4-isoxazolyl) carbonyl]
amino]-7-oxo-4-thia-1- azabicyclo [3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, monosodium
salt.
APPEARANCE
white to off white free flowing crystalline powder
Complies
95.0 - 101.0 % (HPLC)
+198° ~ +221°
RELATED SUBSTANCE
1.0% max (Individual), 5.0% max (total)
WATER
3.5 - 5.5%
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF PENICILLIN
· Penicillic acid [CAS RN: 90-65-3]: an antibiotic substance produced by several species of Penicillium and Aspergillus; a white solid soluble in water; melting point 83 - 84 C; antibiotic and mycotoxin induceing DNA single-strand breaks, toxic to animal tissues also, causing nephrotoxicity and other damage.
· Penicillin G [also called benzylpenicillin, CAS RN: 61-33-6]: the first and the most widely used penicillin compound for medicinal use. It is used in the form of its stable salts (benzathine, potassium, procaine, and sodium) to treat principally the infections due to penicillin-susceptible gram-positive bacteria, gram-negative cocci, Treponema pallidum, and Actinomyces israelii.
· Penicillin G Benzathine [CAS RN: 41372-02-5]: the benzathine salt of penicillin G; having a long-sustained action, administered orally, intramuscularly. Chemically designation is (2S,5R,6R)- 3,3-Dimethyl-7-oxo-6-(2-phenylacetamido)-4-thia-1-azabicyclo [3.2.0] heptane-2-carboxylic acid with N,N' -Dibenzylethylenediamine (2:1). It is a white crystalline powder; slightly soluble in water and sparingly soluble in alcohol.
· Penicillin G Potassium [CAS RN: 113-98-4]: the potassium salt of penicillin G; administered orally and by intravenously. It is a white crystalline powder; odorless, moderately hygroscopic; soluble in water.
· Penicillin G Procaine [CAS RN: 6130-64-9]: the procaine salt of penicillin G; having a long-sustained action, administered intramuscularly. Chemically designation is (2S,5R,6R)- 3,3-Dimethyl-7-oxo-6-(2-phenylacetamido)-4-thia-1-azabicyclo [3.2.0] heptane-2-carboxylic acid with 2-(Diethylamino)ethyl p-aminobenzoate (1:1). It is a white crystalline powder; slightly soluble in water.
· Penicillin G sodium [CAS RN: 69-57-8]: the sodium salt of penicillin G having a potency of 1500–1750 U per mg; administered intramuscularly and intravenously.
· Penicillin N (also called adicillin, CAS RN: 525-94-0]: a cephalosporin that is more active against gram-negative organisms than penicillin G and is highly active against Neisseria; has been used in the treatment of typhoid fever and gonorrhea.
· Penicillin O: similar to penicillin G in antibiotic action but produced by adding a precursor to the culture medium; penicillin O and its potassium and sodium salts are hypoallergenic.
· Penicillin V: [CAS RN: 87-08-1] a semisynthetic penicillin prepared from cultures of the mold Penicillium in the presence of 2-phenoxyethanol with an autolysate of yeast as the source of nitrogen; a white, crystalline powder, soluble in alcohol and acetone; resists destruction by high humidity (gastric juice), thus orally effective.
· Penicillin V Benzathine [CAS RN: 63690-57-3] : the benzathine salt of penicillin V, administered orally. Chemical designation is [2S-(2a,5a,6b)]-3,3 -dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(phenoxyacetyl)amino]-4- thia-1- azabicyclo[3.2.0] heptane-2-carboxylic acid with N,N' -Dibenzylethylenediamine (2:1).
· Penicillin V Potassium [CAS RN: 132-98-9]: the potassium salt of penicillin V, administered orally. Chemical designation is [2S-(2a,5a,6b)]-3,3 -dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(phenoxyacetyl)amino]-4- thia-1- azabicyclo[3.2.0] heptane-2-carboxylic acid, monopotassium salt.